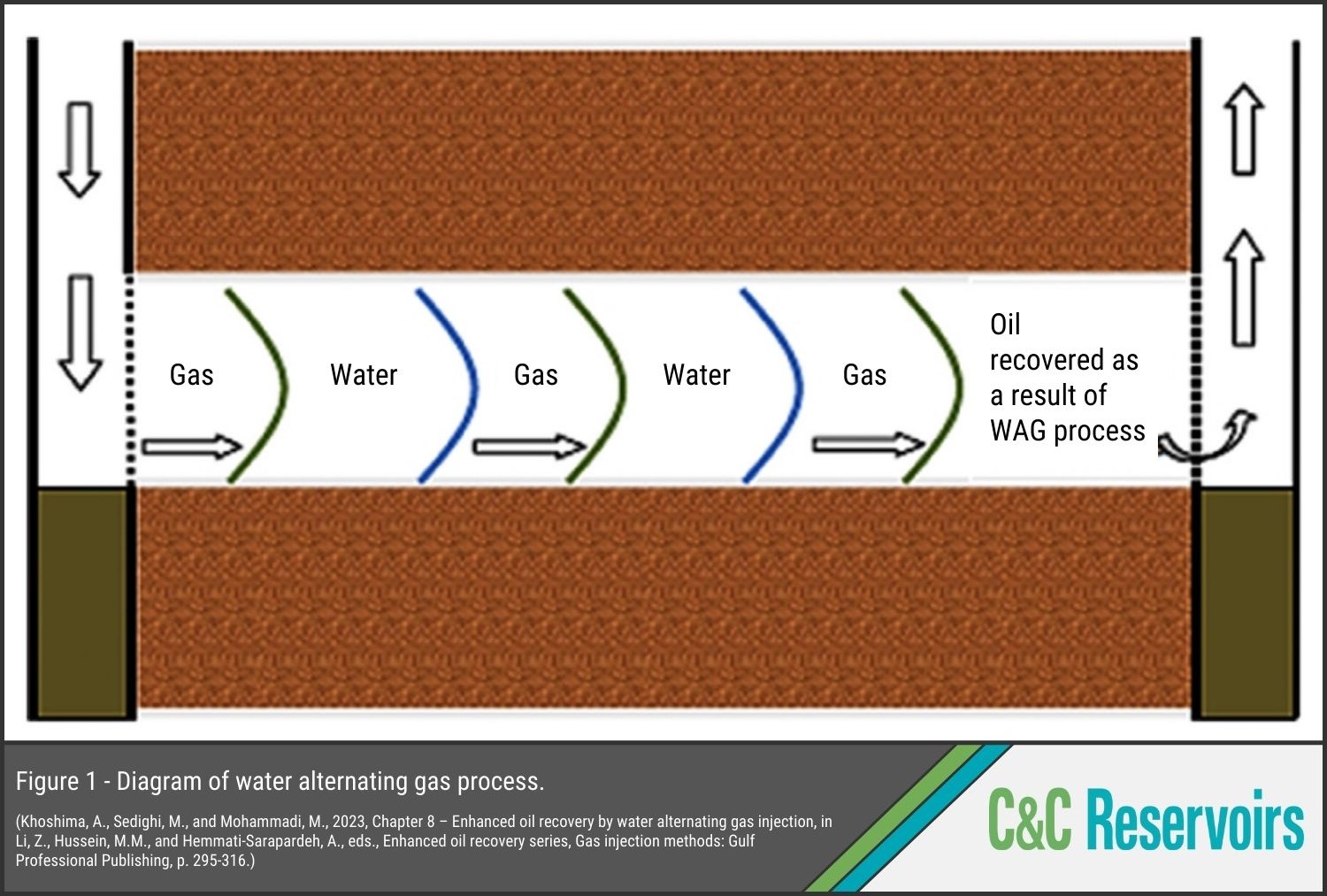
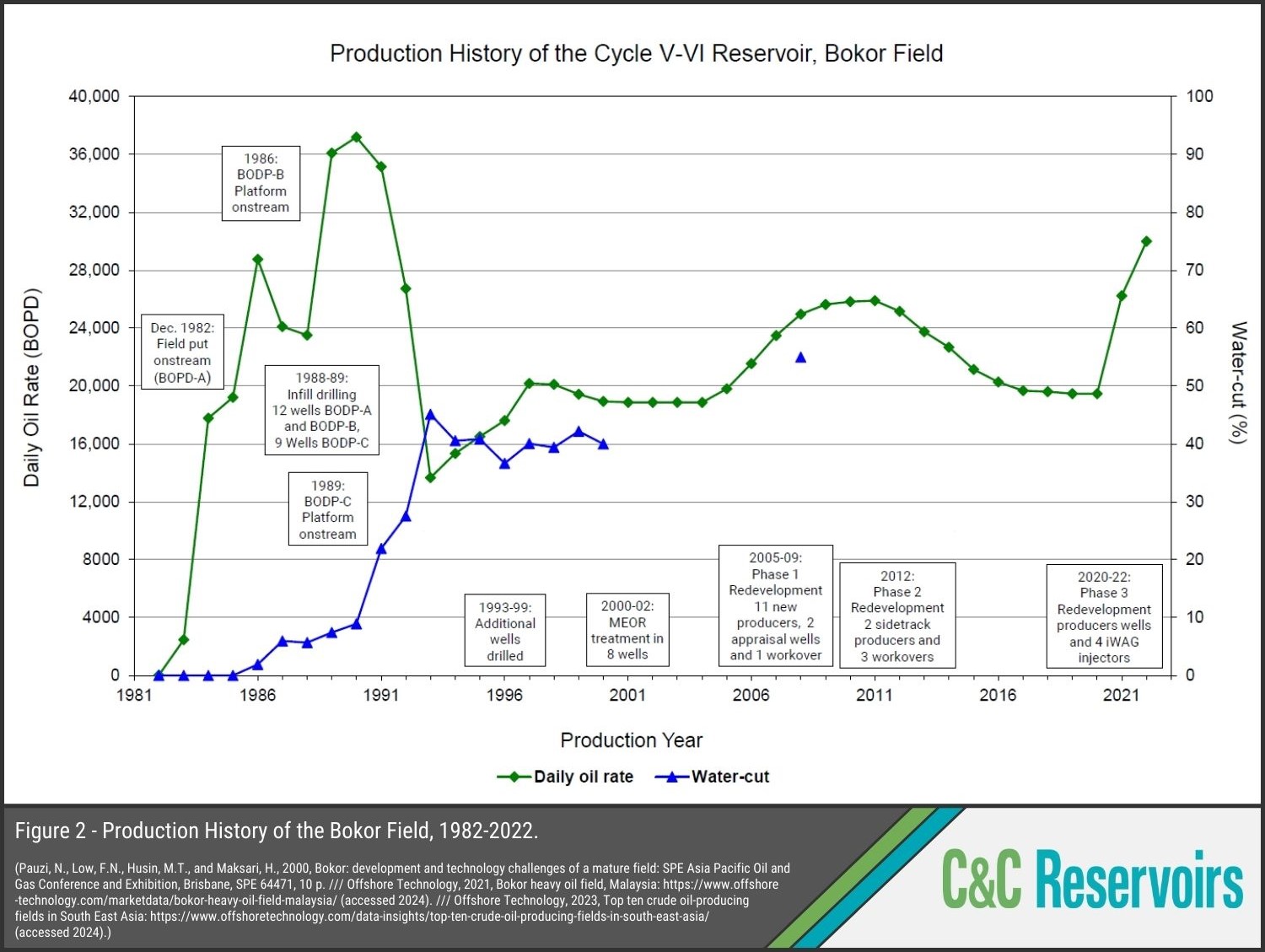
The Bokor Field
Analogue Spotlight
Production from the Bokor Field, offshore Malaysia, began in 1982, 15 years after its discovery. STOIIP and EUR were initially underestimated due to disappointing appraisal results and poor imaging of the complex structure on 2-D seismic. However, acquisition of 3-D seismic and several phases of seismic reinterpretation in the mid-‘90s transformed structural understanding, leading to several STOIIP increases, from a pre-development 100 MMBO to 920 MMBO in 2011. In parallel, recovery factor rose from 14% to 38%. By 2022, 323 MMBO of its EUR of 350 MMBO had been produced.
Development and reservoir management have been challenging. Bokor has 165 stacked sandstone reservoirs within a 6000 ft gross section which includes thief zones and shale barriers/baffles that led to areas of bypassed and residual oil. The shallowest reservoirs are prone to fines migration and sand production, while the oils tend to be viscous, particularly in the shallower reservoirs where the majority of the STOIIP is found.
Several improved recovery methods have been tried, with varying degrees of success. In 2020, the field underwent a third phase of project redevelopment, which involved installation of three new wellhead platforms, and the drilling of new development wells, including four immiscible water-alternating gas (IWAG) injection wells (Fig. 1), which featured intelligent completions and used polymer-based additives. Phase 3 saw production increase to over 10,000 BOPD (Fig. 2), with the improvement attributed to three main factors:
- The IWAG process increased sweep efficiency in the heterogenous reservoir.
- The additives mitigated against fines migration in lower permeability parts of the reservoir.
- The intelligent completions allow active management of injection in real time, negating the need for well intervention.
Want to learn more? Explore best practices and insights from over 150 years of global E&P experience to unlock the full potential of your oil and gas assets with DAKS™.